09 自定义指令和插槽
自定义指令
每个指令都有自己各自独立的功能
- 内置指令:
v-html、v-if、v-bind、v-on… 这都是 Vue 内置的一些指令,可以直接使用 - 自定义指令:同时 Vue 也支持让开发者,自己注册一些指令。这些指令被称为自定义指令
自定义指令介绍
- 概念:自己定义的指令,可以封装一些 DOM 操作,扩展额外的功能
- 在 Vue2.0 中,代码复用和抽象的主要形式是组件。然而,有的情况下,你仍然需要对普通 DOM 元素进行底层操作,这时候就会用到自定义指令。
自定义指令语法
全局注册
js// 在 main.js 中 Vue.directive('指令名', { inserted(el) { // 可以对 el 标签,扩展额外功能 el.focus() }, })局部注册
js// 在 Vue 组件的配置项中 directives: { "指令名": { inserted () { // 可以对 el 标签,扩展额外功能 el.focus() } } }使用指令
- 使用指令语法:
v-指令名。如:<input type="text" v-focus/> - 注册 指令时 不用 加
v-前缀,但 使用时 一定要 加v-前缀
注意
在使用指令的时候,一定要先注册,再使用,否则会报错
- 使用指令语法:
钩子函数
一个指令定义对象可以提供如下几个钩子函数 (均为可选):
bind:只调用一次,指令第一次绑定到元素时调用。在这里可以进行一次性的初始化设置。inserted:被绑定元素插入父节点时调用 (仅保证父节点存在,但不一定已被插入文档中)。update:所在组件的 VNode 更新时调用,但是可能发生在其子 VNode 更新之前。指令的值可能发生了改变,也可能没有。但是你可以通过比较更新前后的值来忽略不必要的模板更新 (详细的钩子函数参数见下)。componentUpdated:指令所在组件的 VNode 及其子 VNode 全部更新后调用。unbind:只调用一次,指令与元素解绑时调用。
钩子函数参数
指令钩子函数会被传入以下参数:
el:指令所绑定的元素,可以用来直接操作 DOM。binding:一个对象,包含以下 property:name:指令名,不包括v-前缀。value:指令的绑定值,例如:v-my-directive="1 + 1"中,绑定值为2。oldValue:指令绑定的前一个值,仅在update和componentUpdated钩子中可用。无论值是否改变都可用。expression:字符串形式的指令表达式。例如v-my-directive="1 + 1"中,表达式为"1 + 1"。arg:传给指令的参数,可选。例如v-my-directive:foo中,参数为"foo"。modifiers:一个包含修饰符的对象。例如:v-my-directive.foo.bar中,修饰符对象为{ foo: true, bar: true }。
vnode:Vue 编译生成的虚拟节点。移步 VNode API 来了解更多详情。oldVnode:上一个虚拟节点,仅在update和componentUpdated钩子中可用。
注意
除了 el 之外,其它参数都应该是只读的,切勿进行修改。如果需要在钩子之间共享数据,建议通过元素的 dataset 来进行。
代码示例
<script>
export default {
/**
* 当页面加载时,该元素将获得焦点 (注意:autofocus 在移动版 Safari 上不工作)
*
* 1. 定义注册指令(全局 or 局部)
* - 全局注册指令(main.ks):Vue.directive('指令名', {指令的配置项})
* - 局部注册指令(App.vue):directives: {指令名:{指令的配置项}}
* 2. 使用指令:v-指令名
*/
// 因为 mounted 钩子函数是在 DOM 元素挂载完成后才执行的,所以此时 DOM 元素已经挂载到页面中了,可以直接获取到 DOM 元素
// 使用 ref 属性给要获取的元素注册一个名字,然后通过 this.$refs.名字 获取到 DOM 元素
// mounted () {
// this.$refs.inp.focus()
// }
// 1.2. 局部注册指令
directives: {
// 指令名:指令的配置项
focus: {
inserted (el) {
el.focus()
},
},
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div id="app">
<h2>自定义指令</h2>
<!-- 2. 使用自定义指令 v-focus -->
<input v-focus ref="inp" type="text" />
</div>
</template>
<style scoped></style>import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// // 1.1. 全局注册指令
// Vue.directive('focus', {
// // inserted 会在 指令所在的元素,被插入到页面中时触发
// inserted (el) {
// // el 就是指令所绑定的元素
// // console.log(el);
// el.focus()
// }
// })
new Vue({
render: (h) => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')总结
自定义指令的作用是什么?
自定义指令可以封装一些 DOM 操作,扩展额外的功能。
自定义指令的作用:
- 修改元素的样式: 可以通过自定义指令来动态修改元素的样式,实现一些特定的视觉效果。
- 绑定事件处理: 可以通过自定义指令实现特定事件的绑定,使元素具有额外的交互行为。
- 操作 DOM: 自定义指令可以用于直接操作 DOM,例如插入、删除、更新 DOM 元素。
- 封装可复用的逻辑: 自定义指令可以封装一些可复用的逻辑,使代码更易维护和组织。
自定义指令通常包含两个生命周期钩子函数:
bind和update。bind钩子在指令绑定到元素时调用update钩子在元素更新时调用。
这两个钩子函数可以用来执行自定义指令的逻辑
vue<template> <div v-custom-directive>Hover me</div> </template> <script> Vue.directive('custom-directive', { bind(el, binding) { // bind 钩子在指令绑定到元素时调用 el.style.backgroundColor = 'lightblue' // 可以通过 binding.value 获取传递给指令的值 if (binding.value) { el.innerHTML = binding.value } }, update(el, binding) { // update 钩子在元素更新时调用 // 可以在这里对元素进行动态更新 }, }) </script>v-custom-directive是自定义指令的使用方式,指令的逻辑定义在Vue.directive中。- 在
bind钩子中,我们改变了元素的背景颜色,并根据传递给指令的值更新了元素的文本内容。
使用自定义指令的步骤是哪两步?
定义注册指令: 在 Vue 实例的选项中或全局注册的指令中,定义自定义指令的行为。通常,你需要使用
Vue.directive方法来注册指令,该方法接受两个参数,指令名称和一个包含钩子函数的对象。js// 使用 Vue.directive 定义了一个名为 customDirective 的自定义指令 // 其中包含了 bind 和 update 钩子 Vue.directive('customDirective', { bind(el, binding) { // bind 钩子,指令绑定到元素时调用的逻辑 }, update(el, binding) { // update 钩子,元素更新时调用的逻辑 }, // 其他钩子和属性... })在模板中使用指令: 在 Vue 模板中,通过使用指令名作为属性来使用自定义指令。可以通过
v-前缀来引用指令,如v-customDirective。vue<!-- 使用 v-customDirective 指令,并通过绑定值传递了一个字符串参数 'Hello, Custom Directive!' --> <template> <div v-customDirective="'Hello, Custom Directive!'">Hover me</div> </template>
自定义指令的绑定值
- 现在需要实现一个 color 指令:传入不同的颜色,给标签设置文字颜色
- 这时候就需要用到自定义指令的绑定值,绑定值就是指令后面的值
v-color="color",这里的color就是绑定值
语法
在绑定指令时,可以通过 "等号" 的形式为指令 绑定 具体的参数值
html<div v-color="color">我是内容</div>通过
binding.value可以拿到指令值,指令值修改会 触发 update 函数jsdirectives: { color: { inserted (el, binding) { el.style.color = binding.value }, update (el, binding) { el.style.color = binding.value } } }
代码示例
<script>
export default {
data () {
return {
bgc: 'pink',
}
},
directives: {
bgc: {
// 当绑定元素插入到 DOM 中
inserted (el, binding) {
// console.log(el, binding);
console.log('自定义指令 v-bgc 的值是:' + binding.value)
el.style.backgroundColor = binding.value
},
// 当绑定元素所在的模板更新时调用
update (el, binding) {
// console.log(el, binding);
console.log('自定义指令 v-bgc 的值修改为:' + binding.value)
el.style.backgroundColor = binding.value
},
},
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div id="app">
<span v-bgc="bgc">自定义指令 v-bgc 的值测试</span> <br /><br />
<button @click="bgc = 'skyblue'">修改 bgc 的值</button>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped></style>import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: (h) => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')案例 v-loading 指令的封装
- 实际开发过程中,发送请求需要时间,在请求的数据未回来时,页面会处于空白状态 => 用户体验不好
- 这时封装一个
v-loading指令,实现加载中的效果
分析
- 本质 loading 效果就是一个蒙层,盖在了盒子上
- 数据请求中,开启 loading 状态,添加蒙层
- 数据请求完毕,关闭 loading 状态,移除蒙层
实现
- 准备一个 loading 类,通过伪元素定位,设置宽高,实现蒙层
- 开启关闭 loading 状态(添加移除蒙层),本质只需要添加移除类即可
- 结合自定义指令的语法进行封装复用
相关代码
<script>
/**
* 获取新闻数据渲染
* 1. 准备一个 loading 类,通过伪元素定位,设置宽高,实现蒙层效果
* 2. 数据请求中,开启 loading 状态,添加蒙层
* 3. 数据请求完毕,关闭 loading 状态,移除蒙层
*/
// 安装 axios:pnpm add axios
import axios from 'axios'
import './index.css'
export default {
data () {
return {
newsList: [],
}
},
// 在 created 钩子函数中发送请求
async created () {
try {
// 发送请求
const res = await axios.get('http://hmajax.itheima.net/api/news')
// 等待 2s 后,将请求到的数据保存到 data 中的 newsList 中(模拟数据请求中的 loading 状态)
setTimeout(() => {
this.newsList = res.data.data
}, 2000)
} catch (err) {
console.dir(err)
}
},
// 自定义指令 v-loading
directives: {
loading: {
inserted (el, binding) {
// 数据请求中,开启 loading 状态; 数据请求完毕,关闭 loading 状态
// console.log(el, binding);
binding.value ? el.classList.add('loading') : el.classList.remove('loading')
},
update (el, binding) {
// 数据请求中,开启 loading 状态; 数据请求完毕,关闭 loading 状态
binding.value ? el.classList.add('loading') : el.classList.remove('loading')
},
},
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div id="app">
<div class="box" v-loading="newsList.length === 0">
<ul>
<li v-for="item in newsList" :key="item.id" class="news">
<div class="left">
<div class="title">{{ item.title }}</div>
<div class="info">
<span>{{ item.source }}</span>
<span>{{ item.time }}</span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="right">
<img :src="item.img" alt="" />
</div>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</template>import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: (h) => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')插槽
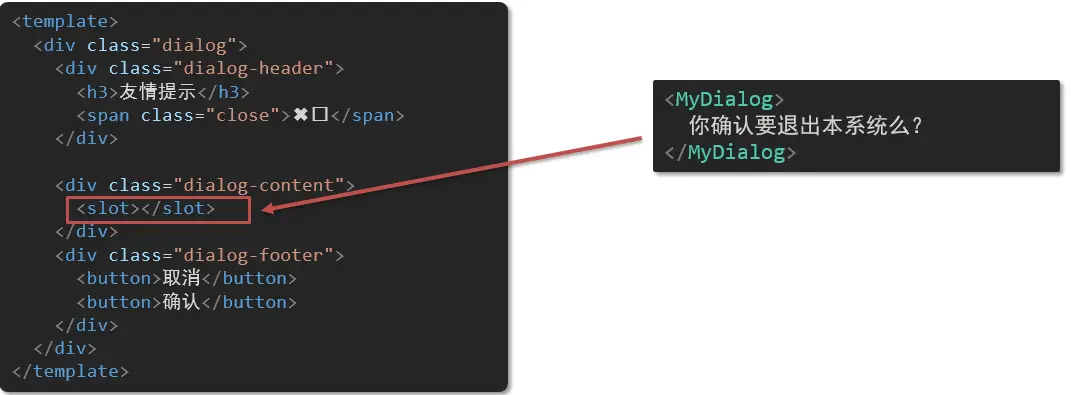
默认插槽
- 将需要多次显示的对话框,封装成一个组件
- 组件的内容部分,不希望写死,希望能使用的时候自定义。怎么办 => 插槽
- 插槽的作用:占位,将来使用组件的时候,填充内容 (让组件内部的一些 结构 支持 自定义)
基本语法
- 组件内需要定制的结构部分,改用
<slot></slot>占位 - 使用组件时,
<MyDialog></MyDialog>标签内部,使用传入结构替换slot - 给插槽传入内容时,可以传入纯文本、html 标签、组件
代码示例
<script>
import './MyDialog.css'
export default {
data () {
return {}
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div class="dialog">
<div class="dialog-header">
<h3>友情提示</h3>
<span class="close">✖️</span>
</div>
<div class="dialog-content">
<!-- 1. 在需要定制的位置,使用 slot 占位 -->
<slot></slot>
</div>
<div class="dialog-footer">
<button>取消</button>
<button>确认</button>
</div>
</div>
</template><script>
/**
* 1. 组件内需要定制的结构部分,改用 <slot></slot> 占位
* 2. 在使用组件时,组件标签内填入内容
*/
import MyDialog from './MyDialog.vue'
export default {
components: {
MyDialog,
},
data () {
return {}
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div>
<!-- 2. 在使用组件时,组件标签内填入内容 -->
<MyDialog>
<div>你确认要删除么</div>
</MyDialog>
<MyDialog>
<p>你确认要退出么</p>
</MyDialog>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
body {
background-color: #b3b3b3;
}
</style>import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: (h) => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')总结
场景:组件内某一部分结构不确定,想要自定义怎么办
- 使用插槽
使用:插槽的步骤分为哪几步?
组件内需要定制的结构部分,改用
<slot></slot>占位vue<div class="dialog-content"> <!-- 1. 在需要定制的位置,使用 slot 占位 --> <slot></slot> </div>在使用组件时,组件标签内填入内容
vue<MyDialog> <div>你确认要删除么</div> </MyDialog> <MyDialog> <p>你确认要退出么</p> </MyDialog>
后备内容
- 通过插槽完成了内容的定制,传什么显示什么,但是如果不传,则是空白
- 能否给插槽设置 默认显示内容 呢? => 使用插槽的 后备内容。
- 后备内容:封装组件时,可以为预留的
<slot>插槽提供后备内容(默认内容)。 - 有时为一个插槽设置具体的后备 (也就是默认的) 内容是很有用的,它只会在没有提供内容的时候被渲染。
语法
在
<slot>标签内,放置内容,作为默认显示内容html<button type="submit"> <!-- 希望这个 <button> 内绝大多数情况下都渲染文本 "Submit" --> <!-- 为了将 "Submit" 作为后备内容,我们可以将它放在 <slot> 标签内 --> <!-- <slot></slot> --> <slot>Submit</slot> </button>现在当我在一个父级组件中使用
<submit-button></submit-button>并且不提供任何插槽内容时,后备内容 "Submit" 将会被渲染:html<button type="submit">Submit</button>如果我们提供内容:
<submit-button>Save</submit-button>则这个提供的内容将会被渲染从而取代后备内容:html<button type="submit">Save</button>
代码示例
<script>
import './MyDialog.css'
export default {
data () {
return {}
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div class="dialog">
<div class="dialog-header">
<h3>友情提示</h3>
<span class="close">✖️</span>
</div>
<div class="dialog-content">
<slot>我是备用内容</slot>
</div>
<div class="dialog-footer">
<button>取消</button>
<button>确认</button>
</div>
</div>
</template><script>
/**
* 后备内容
* 1. 在 `<slot>` 标签内,放置内容,作为默认显示内容
* 2. 在使用组件时,组件标签内填入内容,会替换掉 `<slot>` 标签内的内容
* 3. 如果组件标签内没有填入内容,则显示 `<slot>` 标签内的内容
*/
import MyDialog from './MyDialog.vue'
export default {
components: {
MyDialog,
},
data () {
return {}
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div>
<!-- 填入内容后会替换 slot 里的默认内容 -->
<MyDialog>
<div>你确认要删除么</div>
</MyDialog>
<!-- 没有填入内容的会显示 slot 里默认的内容 -->
<MyDialog> </MyDialog>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
body {
background-color: #b3b3b3;
}
</style>import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: (h) => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')具名插槽

- 一个组件内有多处结构,需要外部传入标签,进行定制 (例如上面的弹框中有三处不同,但是默认插槽只能定制一个位置,这时候怎么办呢?)
- 这时候就需要使用具名插槽,给插槽起一个名字,让外部可以根据名字,进行定制
语法
多个 slot 使用 name 属性区分名字。一个不带 name 的
<slot>出口会带有隐含的名字 "default"。html<!-- 多个 slot 使用 name 属性区分名字:header, content, footer --> <div class="dialog-header"> <slot name="header"></slot> </div> <div class="dialog-content"> <slot name="content"></slot> </div> <div class="dialog-footer"> <slot name="footer"></slot> </div>template配合v-slot:name属性来分发对应标签。在向具名插槽提供内容的时候,我们可以在一个<template>元素上使用 v-slot指令,并以v-slot的参数的形式提供其名称vue<!-- 使用 v-slot:heder/content/footer 来分发对应标签 --> <template v-slot:header> <h3>提示</h3> </template> <template v-slot:content> <p>你确认要删除么</p> </template> <template v-slot:footer> <button>取消</button> <button>确认</button> </template>template可以简写为#(例如:v-slot:header可以简写为#header)vue<template #header> <h3>提示</h3> </template> <template #content> <p>你确认要删除么</p> </template> <template #footer> <button>取消</button> <button>确认</button> </template>
注意
v-slot 只能添加在 <template> 上 (只有 一种例外情况),这一点和已经废弃的 slot attribute 不同。
代码示例
<template>
<div class="dialog">
<div class="dialog-header">
<!-- 一旦插槽起了名字,就是具名插槽,只支持定向分发 -->
<slot name="head"></slot>
</div>
<div class="dialog-content">
<slot name="content"></slot>
</div>
<div class="dialog-footer">
<slot name="footer"></slot>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import './MyDialog.css'
export default {
data () {
return {}
},
}
</script><script>
/**
* 具名插槽
* 1. 在子组件内部,使用 `<slot name="xxx">` 定义插槽
* 2. 在使用子组件时,使用 `<template v-slot:xxx>` 指定插槽内容
* 3. 如果组件内部没有定义插槽,使用 `<template v-slot:xxx>` 会报错
* 4. `<template v-slot:xxx>` 简写为 `<template #xxx>`
*/
import MyDialog from './MyDialog.vue'
export default {
components: {
MyDialog,
},
data () {
return {}
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div>
<MyDialog>
<!-- 需要通过 template 标签包裹需要分发的结构,包成一个整体 -->
<template v-slot:head>
<div>我是大标题</div>
</template>
<template #content>
<div>我是内容</div>
</template>
<template #footer>
<button>取消</button>
<button>确认</button>
</template>
</MyDialog>
</div>
</template>
<style scoped>
body {
background-color: #b3b3b3;
}
</style>import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: (h) => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')总结
组件内 有多处不确定的结构 怎么办?
- 使用具名插槽,给插槽起一个名字,让外部可以根据名字,进行定制
具名插槽的语法是什么?
- 在子组件内部,使用
<slot name="xxx">定义插槽 - 在使用子组件时,使用
<template v-slot:xxx>指定插槽内容
- 在子组件内部,使用
v-slot:插槽名可以简化成什么?<template v-slot:xxx>简写为<template #xxx>
作用域插槽
- 作用域插槽:定义 slot 插槽的同时,是可以传值的。给 插槽 上可以 绑定数据,将来 使用组件时可以用
- 让插槽内容能够访问子组件中才有的数据
插槽分类
插槽只有两种,作用域插槽不属于插槽的一种分类
- 默认插槽
- 具名插槽
语法
给 slot 标签,以 添加属性的方式传值
vue<slot :id="item.id" msg="测试文本"></slot>所有添加的属性,都会被收集到一个对象中
json{ "id": 3, "msg": "测试文本" }在 template 中,通过
#插槽名= "obj"接收,默认插槽名为 defaultvue<MyTable :list="list"> <template #default="obj"> <button @click="del(obj.id)">删除</button> </template> </MyTable>
代码示例
<script>
import './MyTable.css'
export default {
props: {
data: Array,
},
}
</script>
<template>
<table class="my-table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>序号</th>
<th>姓名</th>
<th>年纪</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr v-for="(item, index) in data" :key="item.id">
<td>{{ index + 1 }}</td>
<td>{{ item.name }}</td>
<td>{{ item.age }}</td>
<td>
<!-- 1. 给 slot 标签,添加属性的方式传值 -->
<slot :person="item" msg="测试文本"></slot>
<!-- 2. 将所有的属性,添加到一个对象中 -->
<!--
{
person: { id: 2, name: '孙大明', age: 19 },
msg: '测试文本'
}
-->
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</template><script>
// autocorrect-disable
/**
* 作用域插槽
* 1. 在子组件内部,使用 <slot :属性名="数据"> 将数据传递给父组件
* 2. 父组件使用子组件时,使用 <template v-slot:插槽名="变量名"> 指定插槽内容,通过变量名获取子组件传递的数据 '变量名.属性名'
* 3. <template v-slot:xxx> 简写为 <template #xxx>
* 4. 父组件使用子组件时,可以使用解构赋值的方式,直接获取子组件传递的数据 <template #插槽名="{ 属性名 }">,并将其作为独立的变量在模板中使用
*/
// autocorrect-enable
import MyTable from './MyTable.vue'
export default {
components: {
MyTable,
},
data () {
return {
studentList: [
{ id: 1, name: '张小花', age: 18 },
{ id: 2, name: '孙大明', age: 19 },
{ id: 3, name: '刘德忠', age: 17 },
],
teacherList: [
{ id: 1, name: '赵小云', age: 28 },
{ id: 2, name: '刘蓓蓓', age: 29 },
{ id: 3, name: '姜肖泰', age: 20 },
],
}
},
methods: {
handleDelete (id) {
this.studentList = this.studentList.filter((item) => item.id !== id)
},
handleShow (person) {
console.log('查看', person)
// alert(`姓名:${person.name},年纪:${person.age}`);
console.log(`姓名:${person.name},年纪:${person.age}`)
},
},
}
</script>
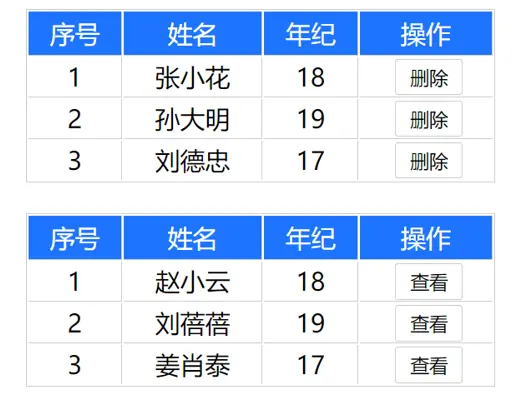
<template>
<div>
<MyTable :data="studentList">
<!-- 给学生列表最后一列添加删除按钮 -->
<template #default="studentProps">
<button @click="handleDelete(studentProps.person.id)">删除</button>
</template>
</MyTable>
<MyTable :data="teacherList">
<!-- 给老师列表最后一列添加查看按钮
- 在 <template v-slot:default="teacherList"> 中,teacherList 是一个对象
- teacherList { person: { id: 2, name: '刘蓓蓓', age: 29 }, msg: '测试文本' }
-->
<template #default="teacherList">
<button @click="handleShow(teacherList.person)">查看</button>
</template>
</MyTable>
<MyTable :data="teacherList">
<!-- 给老师列表最后一列添加查看按钮
- 使用解构赋值的方式直接获取 person 属性
- 从传递的对象中提取 person 属性,并将其作为独立的变量在模板中使用
- 这样可以避免在模板中直接引用整个对象,提高了代码的可读性和灵活性。
-->
<template #default="{ person }">
<button @click="handleShow(person)">查看</button>
</template>
</MyTable>
</div>
</template>import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: (h) => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')总结
作用域插槽的作用是什么?
- 定义 slot 插槽的同时,是可以传值的。给 插槽 上可以 绑定数据,将来 使用组件时可以用
- 插槽内容能够访问子组件中才有的数据
作用域插槽的使用步骤是什么?
- 在子组件内部,使用
<slot :属性名="数据">将数据传递给父组件 - 父组件使用子组件时,使用
<template v-slot:插槽名="变量名">指定插槽内容,通过变量名获取子组件传递的数据变量名.属性名 - 父组件使用子组件时,可以使用解构赋值的方式,直接获取子组件传递的数据
<template #插槽名="{ 属性名 }">,并将其作为独立的变量在模板中使用
- 在子组件内部,使用
综合案例 商品列表
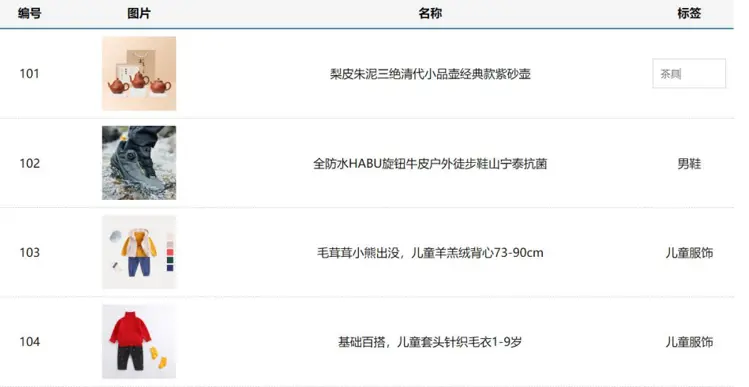
需求说明
my-table 表格组件封装
- 动态传递表格数据渲染
- 表头支持用户自定义
- 主体支持用户自定义
my-tag 标签组件封装
- 双击显示输入框,输入框获取焦点
- 失去焦点,隐藏输入框
- 回显标签信息
- 内容修改,回车 → 修改标签信息
初始化 my-table 局部组件
- 将 my-table 封装成一个局部组件,方便复用
:: code-group
<template>
<div class="table-case">
<MyTable></MyTable>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import MyTable from './MyTable.vue'
export default {
components: {
MyTable,
},
data() {
return {
goods: [
{ id: 101, picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/f8c37ffa41ab1eb84bff499e1f6acfc7.jpg', name: '梨皮朱泥三绝清代小品壶经典款紫砂壶', tag: '茶具' },
{ id: 102, picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/221317c85274a188174352474b859d7b.jpg', name: '全防水 HABU 旋钮牛皮户外徒步鞋山宁泰抗菌', tag: '男鞋' },
{ id: 103, picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/cd4b840751ef4f7505c85004f0bebcb5.png', name: '毛茸茸小熊出没,儿童羊羔绒背心 73-90cm', tag: '儿童服饰' },
{ id: 104, picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/56eb25a38d7a630e76a608a9360eec6b.jpg', name: '基础百搭,儿童套头针织毛衣 1-9 岁', tag: '儿童服饰' },
],
}
},
}
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped>
.table-case {
width: 1000px;
margin: 50px auto;
img {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
object-fit: contain;
vertical-align: middle;
}
}
</style><script>
import './MyTable.less'
</script>
<template>
<table class="my-table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>编号</th>
<th>图片</th>
<th>名称</th>
<th width="100px">标签</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>101</td>
<td><img src="https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/f8c37ffa41ab1eb84bff499e1f6acfc7.jpg" /></td>
<td>梨皮朱泥三绝清代小品壶经典款紫砂壶</td>
<td>
<div class="my-tag">
<!-- <input
class="input"
type="text"
placeholder="输入标签"
/> -->
<div class="text">茶具</div>
</div>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</template>:::
my-table 动态渲染和结构自定义
:data="goods"向 MyTable 子组件传递goods数据,子组件使用props接收type: Array, required: true,- 子组件使用
v-for遍历data数组,为每个item添加key属性 - 使用具名插槽,支持用户自定义表头和主体
- 使用作用域插槽,给插槽绑定数据,将来使用组件时可以用
<template>
<div class="table-case">
<!-- :data="goods" 向 MyTable 子组件传递 goods 数据,子组件使用 props 接收(type: Array, required: true,) -->
<MyTable :data="goods">
<!-- <template v-slot:thead> 具名插槽:给子组件中 name="thead" 的 slot 传递内容 -->
<!-- 这样用户可以自定义表头内容:更换表头内容的顺序 -->
<template v-slot:thead>
<th>编号</th>
<th>图片</th>
<th>名称</th>
<th width="100px">标签</th>
</template>
<!-- #tbody 是一个特殊的语法糖,等价于 v-slot:tbody -->
<!-- 解构赋值语法,用于从父组件传递的数据中提取 item 和 index 两个变量,然后在子组件中直接使用 -->
<template #tbody="{ item, index }">
<td>{{ index + 1 }}</td>
<td><img :src="item.picture" /></td>
<td>{{ item.name }}</td>
<td>
<div class="my-tag">
<!-- <input
class="input"
type="text"
placeholder="输入标签"
/> -->
<div class="text">茶具</div>
</div>
</td>
</template>
</MyTable>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import MyTable from './MyTable.vue'
export default {
components: {
MyTable,
},
data() {
return {
goods: [
{ id: 101, picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/f8c37ffa41ab1eb84bff499e1f6acfc7.jpg', name: '梨皮朱泥三绝清代小品壶经典款紫砂壶', tag: '茶具' },
{ id: 102, picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/221317c85274a188174352474b859d7b.jpg', name: '全防水 HABU 旋钮牛皮户外徒步鞋山宁泰抗菌', tag: '男鞋' },
{ id: 103, picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/cd4b840751ef4f7505c85004f0bebcb5.png', name: '毛茸茸小熊出没,儿童羊羔绒背心 73-90cm', tag: '儿童服饰' },
{ id: 104, picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/56eb25a38d7a630e76a608a9360eec6b.jpg', name: '基础百搭,儿童套头针织毛衣 1-9 岁', tag: '儿童服饰' },
],
}
},
}
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped>
.table-case {
width: 1000px;
margin: 50px auto;
img {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
object-fit: contain;
vertical-align: middle;
}
}
</style><script>
import './MyTable.less'
export default {
name: 'MyTable',
props: {
data: {
type: Array,
required: true,
},
},
}
</script>
<template>
<table class="my-table">
<thead>
<tr>
<!-- 定义名为 thead 的 slot 插槽 -->
<slot name="thead"></slot>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<!-- 使用 v-for 遍历 data 数组,为每个 item 添加 key 属性 -->
<tr v-for="(item, index) in data" :key="item.id">
<!-- 定义名为 tbody 的 slot 插槽,并向父组件传递 item 和 index 数据 -->
<slot name="tbody" :item="item" :index="index"></slot>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</template>封装 my-tag 局部组件
将 my-tag 封装成一个局部组件,方便复用
使用
v-if和v-else实现双击@dbclick显示输入框,输入框获取焦点,失去焦点@blur,隐藏输入框输入框自动聚焦:
ref="input"获取输入框元素,封装v-focus自定义指令,使用inserted钩子函数,el.focus()获取焦点v-focus自定义指令的使用:<input type="text" v-focus />v-focus自定义指令的注册:Vue.directive('focus', { inserted(el) { el.focus() } })- 因为 vue 是异步渲染,所以需要在
nextTick中获取焦点this.$nextTick(() => { this.$refs.input.focus() })
回显标签信息:
@keyup.enter回车事件,修改标签信息v-model实现功能 (简化代码)v-model=>:value和@input- 因为回显的标签信息属于父组件传递的数据,所以不能使用
v-model="tag"双向绑定tag数据,而是需要使用this.$emit('input', e.target.value)向父组件传递数据
代码示例
<script>
import './MyTable.less'
export default {
name: 'MyTable',
props: {
data: {
type: Array,
required: true,
},
},
}
</script>
<template>
<table class="my-table">
<thead>
<tr>
<!-- 定义名为 thead 的 slot 插槽 -->
<slot name="thead"></slot>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<!-- 使用 v-for 遍历 data 数组,为每个 item 添加 key 属性 -->
<tr v-for="(item, index) in data" :key="item.id">
<!-- 定义名为 tbody 的 slot 插槽,并向父组件传递 item 和 index 数据 -->
<slot name="tbody" :item="item" :index="index"></slot>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</template><script>
import './MyTag.less'
export default {
name: 'MyTag',
props: {
value: {
type: String,
required: true,
},
},
data () {
return {
isEdit: false,
}
},
methods: {
handleEnter () {
// 非空处理
if (this.$refs.inp.value.trim() === '') {
console.log('标签不能为空')
return
}
// 通过 $emit() 方法触发 input 事件,将 <input> 元素的值传递给父组件
this.$emit('input', this.$refs.inp.value)
this.isEdit = false
},
handleEdit () {
this.isEdit = true
// 直接注册为全局指令 v-focus,不需要使用 $nextTick
// this.$nextTick(() => {
// this.$refs.inp.focus()
// })
},
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div class="my-tag">
<!-- 默认为显示文本,所以 isEdit 为 false -->
<!--
- v-if 当 isEdit 为 true 时显示 <input> 元素
- :value 将 value 变量的值绑定到 <input> 元素的 value 属性上
- v-focus 自定义指令,当 <input> 元素被渲染时,它会自动获得焦点
- ref="inp" 给 <input> 元素注册一个引用,方便通过 this.$refs.inp 来访问这个元素(使用 this.$refs.inp.value 获取 <input> 元素的值)和使用 focus() 方法
- @blur 事件监听器,当 <input> 元素失去焦点时,将 isEdit 设置为 false
- @keyup.enter 事件监听器,当用户按下回车键时,调用 handleEnter() 方法
-->
<input v-if="isEdit" :value="value" v-focus ref="inp" @blur="isEdit = false" @keyup.enter="handleEnter" class="input" type="text" placeholder="输入标签" />
<div v-else @dblclick="isEdit = true" class="text">{{ value }}</div>
</div>
</template><template>
<div class="table-case">
<!-- :data="goods" 向 MyTable 子组件传递 goods 数据,子组件使用 props 接收(type: Array, required: true,) -->
<MyTable :data="goods">
<!-- <template v-slot:thead> 具名插槽:给子组件中 name="thead" 的 slot 传递内容 -->
<!-- 这样用户可以自定义表头内容:更换表头内容的顺序 -->
<template v-slot:thead>
<th>编号</th>
<th>图片</th>
<th>名称</th>
<th width="100px">标签</th>
</template>
<!-- #tbody 是一个特殊的语法糖,等价于 v-slot:tbody -->
<!-- 解构赋值语法,用于从父组件传递的数据中提取 item 和 index 两个变量,然后在子组件中直接使用 -->
<template #tbody="{ item, index }">
<td>{{ index + 1 }}</td>
<td><img :src="item.picture" /></td>
<td>{{ item.name }}</td>
<td>
<!-- 父组件中使用 v-model 的前提是子组件必须使用 value 接受值,提交事件名为 @input -->
<MyTag v-model="item.tag"></MyTag>
</td>
</template>
</MyTable>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import MyTable from './MyTable.vue'
import MyTag from './MyTag.vue'
export default {
components: {
MyTable,
MyTag,
},
data () {
return {
goods: [
{ id: 101, picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/f8c37ffa41ab1eb84bff499e1f6acfc7.jpg', name: '梨皮朱泥三绝清代小品壶经典款紫砂壶', tag: '茶具' },
{ id: 102, picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/221317c85274a188174352474b859d7b.jpg', name: '全防水 HABU 旋钮牛皮户外徒步鞋山宁泰抗菌', tag: '男鞋' },
{ id: 103, picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/cd4b840751ef4f7505c85004f0bebcb5.png', name: '毛茸茸小熊出没,儿童羊羔绒背心 73-90cm', tag: '儿童服饰' },
{ id: 104, picture: 'https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/56eb25a38d7a630e76a608a9360eec6b.jpg', name: '基础百搭,儿童套头针织毛衣 1-9 岁', tag: '儿童服饰' },
],
}
},
}
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped>
.table-case {
width: 1000px;
margin: 50px auto;
img {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
object-fit: contain;
vertical-align: middle;
}
}
</style>import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// 注册自定义指令 v-focus
Vue.directive('focus', {
// 当绑定元素插入到 DOM 中。
inserted: (el) => {
// 聚焦元素
el.focus()
},
})
new Vue({
render: (h) => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')单页应用程序
单页应用程序:SPA【Single Page Application】是指所有的功能都在一个 html 页面上实现
具体示例
- 单页应用网站: 网易云音乐 https://music.163.com/
- 多页应用网站:京东 https://jd.com/
单页应用 VS 多页面应用
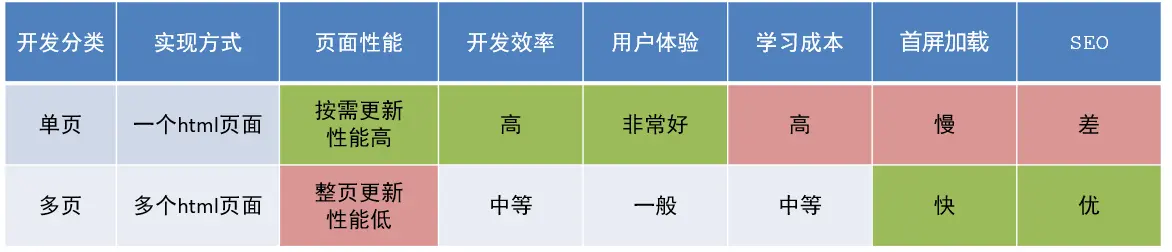
- 单页应用类网站:系统类网站 / 内部网站 / 文档类网站 / 移动端站点
- 多页应用类网站:公司官网 / 电商类网站
总结
什么是单页面应用程序?
- 所有功能在一个 html 页面上实现
单页面应用优缺点?
- 优点:按需更新性能高,开发效率高,用户体验好
- 缺点:学习成本,首屏加载慢,不利于 SEO
应用场景?
- 系统类网站 / 内部网站 / 文档类网站 /移动端站点