12 状态管理 Vuex
Vuex
- Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。
- Vuex 也集成到 Vue 的官方调试工具 devtools extension,提供了诸如零配置的 time-travel 调试、状态快照导入导出等高级调试功能。
Vuex 是什么
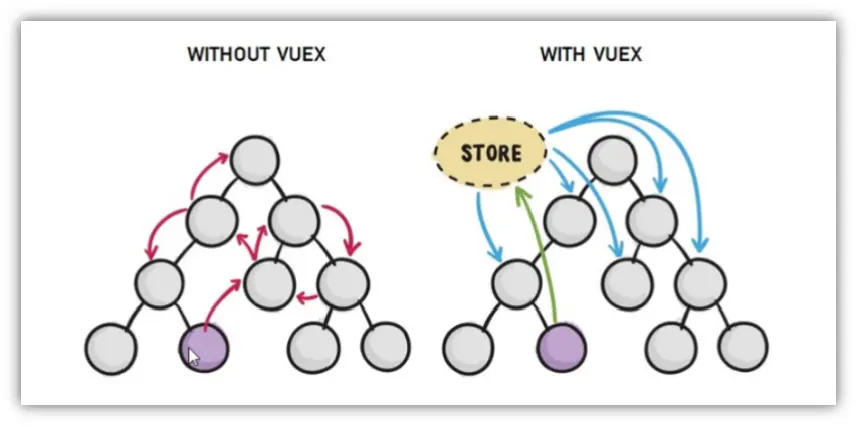
- Vuex 是一个 Vue 的 状态管理工具,状态就是数据。
- 大白话:Vuex 是一个插件,可以帮我们管理 Vue 通用的数据 (多组件共享的数据)。例如:购物车数据 个人信息数
使用场景
- 某个状态 在 很多个组件 来使用 (个人信息)
- 多个组件 共同维护 一份数据 (购物车)
优势
- 共同维护一份数据,数据集中化管理
- 响应式变化
- 操作简洁 (vuex 提供了一些辅助函数)
注意
- 如果您不打算开发大型单页应用,使用 Vuex 可能是繁琐冗余的。
- 不是所有的场景都适用于 vuex,只有在必要的时候才使用 vuex
- 使用了 vuex 之后,会附加更多的框架中的概念进来,增加了项目的复杂度(数据的操作更便捷,数据的流动更清晰)
Vuex 就像《近视眼镜》, 你自然会知道什么时候需要用它~
准备章节代码
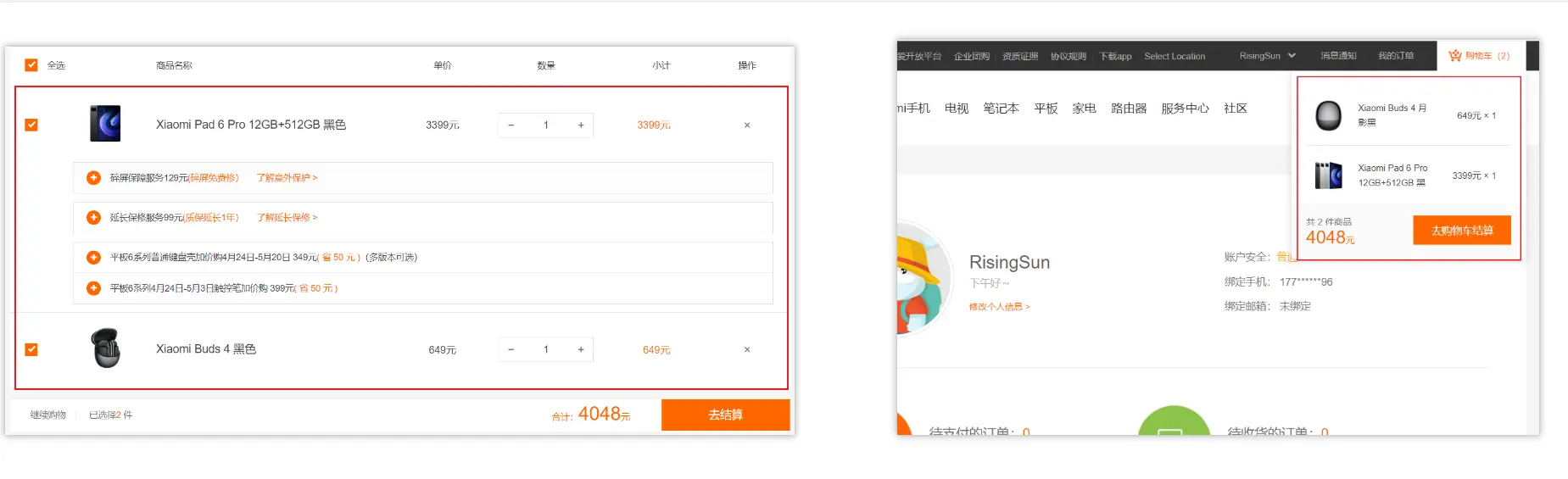
需求:多组件共享数据
目标:基于脚手架创建项目,构建 vuex 多组件数据共享环境
效果是三个组件共享一份数据:
- 任意一个组件都可以修改数据
- 三个组件的数据是同步的
使用
create-vue创建项目bashpnpm create vue@legacy删除
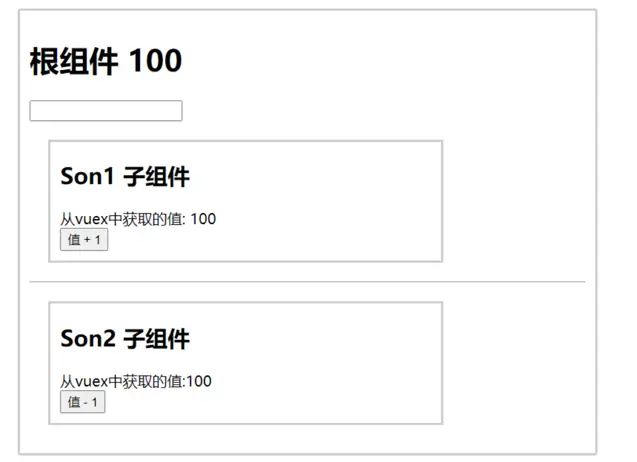
src目录下所有文件,准备三个组件(App.vue、Son1.vue和Son2.vue)和main.js入口文件bashrm -rf src/* mkdir src/components touch src/App.vue src/components/Son1.vue src/components/Son2.vue src/main.js准备代码
vue<script> import Son1 from './components/Son1.vue' import Son2 from './components/Son2.vue' export default { name: 'App', components: { Son1, Son2, }, data() { return {} }, } </script> <template> <div id="app"> <h1>根组件</h1> <input type="text"> <Son1 /> <hr> <Son2 /> </div> </template> <style> #app { width: 600px; margin: 20px auto; border: 3px solid #ccc; border-radius: 3px; padding: 10px; } </style>jsimport Vue from 'vue' import App from './App.vue' Vue.config.productionTip = false new Vue({ render: h => h(App), }).$mount('#app')vue<script> export default { name: 'Son1Com', } </script> <template> <div class="box"> <h2>Son1 子组件</h2> 从 vuex 中获取的值:<label /> <br> <button>值 + 1</button> </div> </template> <style lang="css" scoped> .box { border: 3px solid #ccc; width: 400px; padding: 10px; margin: 20px; } h2 { margin-top: 10px; } </style>vue<script> export default { name: 'Son2Com', } </script> <template> <div class="box"> <h2>Son2 子组件</h2> 从 vuex 中获取的值:<label /> <br> <button>值 - 1</button> </div> </template> <style lang="css" scoped> .box { border: 3px solid #ccc; width: 400px; padding: 10px; margin: 20px; } h2 { margin-top: 10px; } </style>此时项目目录为
bash❯ tre -E node_modules . ├── eslint.config.js ├── package.json ├── pnpm-lock.yaml ├── public │ └── favicon.ico ├── src │ ├── App.vue │ ├── components │ │ ├── Son1.vue │ │ └── Son2.vue │ └── main.js └── vite.config.js
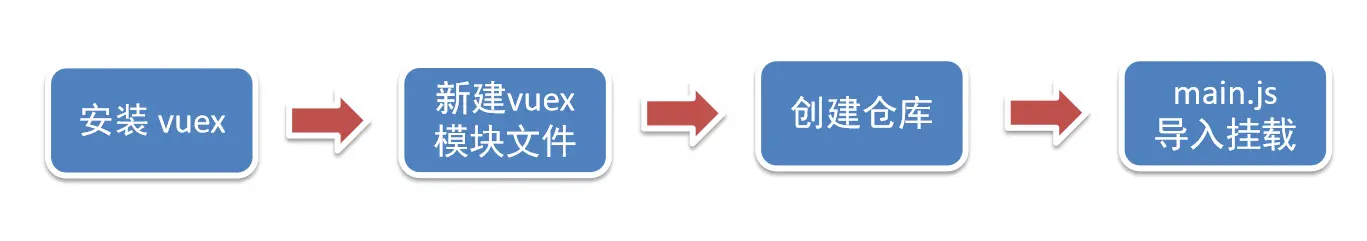
vuex 的使用
每一个 Vuex 应用的核心就是 store(仓库)。"store" 基本上就是一个容器,它包含着你的应用中大部分的状态 (state)。Vuex 和单纯的全局对象有以下两点不同:
- Vuex 的状态存储是响应式的。当 Vue 组件从 store 中读取状态的时候,若 store 中的状态发生变化,那么相应的组件也会相应地得到高效更新。
- 你不能直接改变 store 中的状态。改变 store 中的状态的唯一途径就是显式地提交 (commit) mutation。这样使得我们可以方便地跟踪每一个状态的变化,从而让我们能够实现一些工具帮助我们更好地了解我们的应用。
安装 vuex
安装
vuex与vue-router类似,vuex是一个独立存在的插件,如果脚手架初始化没有选vuex,就需要额外安装。bashpnpm add vuex@3
新建 vuex 模块文件
- 新建
store/index.js专门存放vuex - 为了维护项目目录的整洁,在
src目录下新建一个store目录其下放置一个index.js文件。 (和router/index.js类似)
❯ tre .\src\
.\src\
├── App.vue
├── components
│ ├── Son1.vue
│ └── Son2.vue
├── main.js # 挂载使用 vuex
└── store
└── index.js # 定义 vuex新建仓库
// 导入 vue 和 vuex
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// vuex 也是 vue 的插件,需要 use 一下,进行插件的安装初始化
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建仓库 store
const store = new Vuex.Store()
// 导出仓库
export default storemain.js 导入挂载
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import store from './store'
测试打印 Vuex
<script>
import Son1 from './components/Son1.vue'
import Son2 from './components/Son2.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
Son1,
Son2,
},
data() {
return {}
},
created() {
// console.log('this.$route', this.$route) // undefined 我们没使用路由管理组件
console.log('this.$store', this.$store)
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>根组件</h1>
<input type="text">
<Son1 />
<hr>
<Son2 />
</div>
</template>
<style>
#app {
width: 600px;
margin: 20px auto;
border: 3px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 3px;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>state 状态
- 目标:明确如何给仓库 提供 数据,如何 使用 仓库的数据
单一状态树
- Vuex 使用单一状态树——是的,用一个对象就包含了全部的应用层级状态。至此它便作为一个 "唯一数据源 (SSOT)" 而存在。这也意味着,每个应用将仅仅包含一个 store 实例。单一状态树让我们能够直接地定位任一特定的状态片段,在调试的过程中也能轻易地取得整个当前应用状态的快照。
- 单状态树和模块化并不冲突——在后面的章节里我们会讨论如何将状态和状态变更事件分布到各个子模块中。
- 存储在 Vuex 中的数据和 Vue 实例中的
data遵循相同的规则,例如状态对象必须是纯粹 (plain) 的。参考:Vue#data。
提供数据
State 提供唯一的公共数据源,所有共享的数据都要统一放到 Store 中的 State 中存储。
state状态,即数据,类似于 vue 组件中的data打开项目中的
store.js文件,在state对象中可以添加我们要共享的数据。jsconst store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 101, }, })state vs data
data是组件自己的数据,state中的数据整个 vue 项目的组件都能访问到
访问 Vuex 中的数据
在组件中获取 state 对象中的共享数据 count?
通过
$store直接访问- 模板中:
{{ $store.state.xxx }} - 组件逻辑中:
this.$store.state.xxx - JS 模块中:
store.state.xxx
- 模板中:
组件内通过辅助函数
mapState映射计算属性从 store 实例中读取状态最简单的方法就是在 计算属性 中返回某个状态
jsx<h1>state 的数据 - {{ count }}</h1> computed: { count () { return store.state.count } }- 每当
store.state.count变化的时候,都会重新求取计算属性,并且触发更新相关联的 DOM。 - 然而,这种模式导致组件依赖全局状态单例。在模块化的构建系统中,在每个需要使用 state 的组件中需要频繁地导入,并且在测试组件时需要模拟状态。
- 每当
示例代码
<script>
import Son1 from './components/Son1.vue'
import Son2 from './components/Son2.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
Son1,
Son2,
},
data() {
return {}
},
computed: {
count() {
return this.$store.state.count
},
},
created() {
// console.log('this.$route', this.$route) // undefined 我们没使用路由管理组件
console.log('this.$store', this.$store)
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>根组件 - {{ $store.state.title }} - {{ count }}</h1>
<input type="text">
<Son1 />
<hr>
<Son2 />
</div>
</template>
<style>
#app {
width: 600px;
margin: 20px auto;
border: 3px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 3px;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import store from './store'
console.log('store.state.count', store.state.count)
console.log('store.state.title', store.state.title)
// 导入 vue 和 vuex
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// vuex 也是 vue 的插件,需要 use 一下,进行插件的安装初始化
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建仓库 store
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 101,
title: '我是 store 中的标题',
},
})
// 导出仓库
export default storemapState 辅助函数

当一个组件需要获取多个状态的时候,将这些状态都声明为计算属性会有些重复和冗余。为了解决这个问题,我们可以使用
mapState辅助函数帮助我们生成计算属性。mapState函数返回的是一个对象。使用步骤:
导入 mapState (mapState 是 vuex 中的一个函数)
jsx// 在单独构建的版本中辅助函数为 Vuex.mapState import { mapState } from 'vuex'采用数组形式引入 state 属性
当映射的计算属性的名称与 state 的子节点名称相同时,我们也可以给 mapState 传一个字符串数组
js// 映射 this.count 为 store.state.count computed: mapState(['count']) // 等价于 // computed: { // count() { // return this.$store.state.count // }, // },完整写法
jscomputed: mapState({ // 箭头函数可使代码更简练 count: (state) => state.count, // 传字符串参数 'count' 等同于 `state => state.count` countAlias: 'count', // 为了能够使用 `this` 获取局部状态,必须使用常规函数 countPlusLocalState(state) { return state.count + this.localCount }, })
对象展开运算符
mapState函数返回的是一个对象。我们如何将它与局部计算属性混合使用呢?- 通常,我们需要使用一个工具函数将多个对象合并为一个,以使我们可以将最终对象传给
computed属性。但是自从有了 对象展开运算符,我们可以极大地简化写法。
computed: {
// 使用对象展开运算符将此对象混入到外部对象中
...mapState(['count'])
title() {
return this.$store.state.title
}
}示例代码
<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
import Son1 from './components/Son1.vue'
import Son2 from './components/Son2.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
Son1,
Son2,
},
computed: {
...mapState(['title']),
count() {
return this.$store.state.count
},
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>根组件 - {{ title }} - {{ count }}</h1>
<input type="text">
<Son1 />
<hr>
<Son2 />
</div>
</template>
<style>
#app {
width: 600px;
margin: 20px auto;
border: 3px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 3px;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>组件仍然保有局部状态
- 使用 Vuex 并不意味着你需要将所有的状态放入 Vuex。
- 虽然将所有的状态放到 Vuex 会使状态变化更显式和易调试,但也会使代码变得冗长和不直观。如果有些状态严格属于单个组件,最好还是作为组件的局部状态。
- 你应该根据你的应用开发需要进行权衡和确定。
Getter 全局计算属性
有时候我们需要从 store 中的 state 中派生出一些状态,例如对列表进行过滤并计数:
computed: {
doneTodosCount () {
return this.$store.state.todos.filter(todo => todo.done).length
}
}如果有多个组件需要用到此属性,我们要么复制这个函数,或者抽取到一个共享函数然后在多处导入它——无论哪种方式都不是很理想。
Vuex 允许我们在 store 中定义 "getter"(可以认为是 store 的计算属性)。就像计算属性一样,getter 的返回值会根据它的依赖被缓存起来,且只有当它的依赖值发生了改变才会被重新计算。
Getter 接受 state 作为其第一个参数:
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
todos: [
{ id: 1, text: '...', done: true },
{ id: 2, text: '...', done: false },
],
},
getters: {
doneTodos: (state) => {
return state.todos.filter((todo) => todo.done)
},
},
})getter vs computed
computed主要用于组件内的计算属性。computed属性是响应式的,当依赖的状态发生变化时,它会自动重新计算。这使得computed属性在模板中可以像普通属性一样使用,而且只有在需要时才会重新计算。getters主要用于全局状态管理,对 store 中的 state 进行计算或派生。getters返回的值会被缓存,只有当依赖的 state 发生变化时,它才会重新计算。- 在 Vuex 中,
getters提供了一种更结构化和集中式的方式来处理状态的计算逻辑。
通过属性访问
Getter 会暴露为 store.getters 对象,你可以以属性的形式访问这些值:
store.getters.doneTodos // -> [{ id: 1, text: '...', done: true }]Getter 也可以接受其他 getter 作为第二个参数:
getters: {
// ...
doneTodosCount: (state, getters) => {
return getters.doneTodos.length
}
}
store.getters.doneTodosCount // -> 1我们可以很容易地在任何组件中使用它:
computed: {
doneTodosCount () {
return this.$store.getters.doneTodosCount
}
}注意
getter 在通过属性访问时是作为 Vue 的响应式系统的一部分缓存其中的。
通过方法访问
你也可以通过让 getter 返回一个函数,来实现给 getter 传参。在你对 store 里的数组进行查询时非常有用。
getters: {
// ...
getTodoById: (state) => (id) => {
return state.todos.find((todo) => todo.id === id)
}
}
store.getters.getTodoById(2) // -> { id: 2, text: '...', done: false }注意
getter 在通过方法访问时,每次都会去进行调用,而不会缓存结果。
mapGetters 辅助函数
mapGetters 辅助函数仅仅是将 store 中的 getter 映射到局部计算属性:
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
computed: {
// 使用对象展开运算符将 getter 混入 computed 对象中
...mapGetters([
'doneTodosCount',
'anotherGetter',
// ...
]),
},
}如果你想将一个 getter 属性另取一个名字,使用对象形式:
...mapGetters({
// 把 `this.doneCount` 映射为 `this.$store.getters.doneTodosCount`
doneCount: 'doneTodosCount'
})示例代码
<script>
import { mapGetters, mapState } from 'vuex'
import Son1 from './components/Son1.vue'
import Son2 from './components/Son2.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
Son1,
Son2,
},
computed: {
...mapState(['title', 'count', 'numList']),
...mapGetters(['oddNums']),
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>根组件 - {{ title }} - {{ count }}</h1>
<p>numList: {{ numList }}</p>
<input type="text">
<Son1 />
<hr>
<Son2 />
<hr>
<p>numList 中的奇数:<span>{{ oddNums }}</span></p>
</div>
</template>
<style>
#app {
width: 600px;
margin: 20px auto;
border: 3px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 3px;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 101,
title: '我是 store 中的标题',
numList: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10],
},
getters: {
bigNums: state => (num) => {
return state.numList.filter(item => item > num)
},
evenNums: (state) => {
return state.numList.filter(item => item % 2 === 0).join(', ')
},
oddNums: (state) => {
return state.numList.filter(item => item % 2 !== 0).join(', ')
},
},
})
export default store<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Son1Com',
computed: {
...mapState(['count']),
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div class="box">
<h2>Son1 子组件</h2>
从 vuex 中获取的值:<label>{{ count }}</label>
<br>
<p>numList 中大于 6 的数:<span>{{ $store.getters.bigNums(6) }}</span></p>
<p>numList 中的偶数:<span>{{ $store.getters.evenNums }}</span></p>
</div>
</template>
<style lang="css" scoped>
.box {
border: 3px solid #ccc;
width: 400px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 20px;
}
h2 {
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style><script>
import { mapGetters, mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Son2Com',
computed: {
// mapState 和 mapGetters 都是映射属性
...mapState(['count']),
...mapGetters(['bigNums', 'evenNums']),
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div class="box">
<h2>Son2 子组件</h2>
从 vuex 中获取的值:<span>{{ count }}</span>
<br>
<p>numList 中大于 5 的数:<span>{{ bigNums(5) }}</span></p>
<p>numList 中的偶数:<span>{{ evenNums }}</span></p>
</div>
</template>
<style lang="css" scoped>
.box {
border: 3px solid #ccc;
width: 400px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 20px;
}
h2 {
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>Mutation 提交
由于 store 中的状态是响应式的,在组件中调用 store 中的状态简单到仅需要在计算属性中返回即可。触发变化也仅仅是在组件的 methods 中提交 mutation。
一条重要的原则就是要记住 mutation 必须是同步函数。
在 Vuex 中,mutation 都是同步事务:
jsstore.commit('increment') // 任何由 "increment" 导致的状态变更都应该在此刻完成
Vuex 的单项数据流
- vuex 同样遵循单向数据流,组件中不能直接修改仓库的数据
- 再次强调,我们通过提交 mutation 的方式,而非直接改变
store.state.count,是因为我们想要更明确地追踪到状态的变化。这个简单的约定能够让你的意图更加明显,这样你在阅读代码的时候能更容易地解读应用内部的状态改变。此外,这样也让我们有机会去实现一些能记录每次状态改变,保存状态快照的调试工具。有了它,我们甚至可以实现如时间穿梭般的调试体验。
开启严格模式
通过
strict: true可以开启严格模式,开启严格模式后,直接修改 state 中的值会报错jsconst store = new Vuex.Store({ // ... strict: true, })state 数据的修改只能通过 mutations,并且 mutations 必须是同步的
在严格模式下,无论何时发生了状态变更且不是由 mutation 函数引起的,将会抛出错误。这能保证所有的状态变更都能被调试工具跟踪到。
严格模式有利于初学者,检测不规范的代码。但是不要在发布环境下启用严格模式!严格模式会深度监测状态树来检测不合规的状态变更——请确保在发布环境下关闭严格模式,以避免性能损失。
jsconst store = new Vuex.Store({ // ... strict: process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production', })
示例代码
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// 严格模式
// 有利于初学者,检测不规范的代码。但是 不要在发布环境下启用严格模式!
// 严格模式会深度监测状态树来检测不合规的状态变更
// 请确保在发布环境下关闭严格模式,以避免性能损失
strict: process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production',
state: {
count: 101,
title: '我是 store 中的标题',
},
})
export default store<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Son1Com',
computed: {
...mapState(['count']),
},
methods: {
handleAdd() {
// 开启严格模式后,下面这行代码会报错:// [!code highlight:3]
// Error: [vuex] do not mutate vuex store state outside mutation handlers.
this.$store.state.count++
},
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div class="box">
<h2>Son1 子组件</h2>
从 vuex 中获取的值:<label>{{ count }}</label>
<br>
<button @click="handleAdd">
值 + 1
</button>
</div>
</template>
<style lang="css" scoped>
.box {
border: 3px solid #ccc;
width: 400px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 20px;
}
h2 {
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>更改 Vuex 的 store 中的状态
更改 Vuex 的 store 中的状态的唯一方法是提交 mutation。
Vuex 中的 mutation 非常类似于事件:每个 mutation 都有一个字符串的 事件类型 (type) 和 一个 回调函数 (handler)。这个回调函数就是我们实际进行状态更改的地方,并且它会接受 state 作为第一个参数
jsconst store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 1, }, mutations: { increment(state) { // 变更状态 state.count++ }, }, })你不能直接调用一个 mutation handler。这个选项更像是事件注册:"当触发一个类型为
increment的 mutation 时,调用此函数。" 要唤醒一个 mutation handler,你需要以相应的 type 调用 store.commit 方法:jsstore.commit('increment')
提交载荷 Payload
你可以向
store.commit传入额外的参数,即 mutation 的 载荷(payload)js// ... mutations: { increment (state, n) { state.count += n } } // 调用 store.commit 方法 store.commit('increment', 10)在大多数情况下,载荷应该是一个对象,这样可以包含多个字段并且记录的 mutation 会更易读
js// ... mutations: { increment (state, payload) { state.count += payload.amount } } // 调用 store.commit 方法 store.commit('increment', { amount: 10 })
对象风格的提交方式
提交 mutation 的另一种方式是直接使用包含
type属性的对象:jsstore.commit({ type: 'increment', amount: 10, })当使用对象风格的提交方式,整个对象都作为载荷传给 mutation 函数,因此 handler 保持不变:
jsmutations: { increment (state, payload) { state.count += payload.amount } }
Mutation 需遵守 Vue 的响应规则
既然 Vuex 的 store 中的状态是响应式的,那么当我们变更状态时,监视状态的 Vue 组件也会自动更新。这也意味着 Vuex 中的 mutation 也需要与使用 Vue 一样遵守一些注意事项:
最好提前在你的 store 中初始化好所有所需属性。
当需要在对象上添加新属性时,你应该
使用
Vue.set(obj, 'newProp', 123)或者以新对象替换老对象。例如,利用 对象展开运算符 我们可以这样写:
jsstate.obj = { ...state.obj, newProp: 123 }
mapMutations 辅助函数
- 你可以在组件中使用
this.$store.commit('xxx')提交 mutation - 使用
mapMutations辅助函数将组件中的 methods 映射为store.commit调用(需要在根节点注入store)。
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
methods: {
...mapMutations([
'increment', // 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
// `mapMutations` 也支持载荷:
'incrementBy', // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
...mapMutations({
add: 'increment', // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
}),
},
}示例代码
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
strict: process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production',
state: {
count: 101,
title: '我是 store 中的标题',
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++
},
decrement(state) {
state.count--
},
incrementBy(state, num) {
state.count += num
},
decrementBy(state, payload) {
state.count -= payload.amount
},
changeTitle(state, title) {
state.title = title
},
},
})
export default store<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Son1Com',
computed: {
...mapState(['count']),
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div class="box">
<h2>Son1 子组件</h2>
从 vuex 中获取的值:<label>{{ count }}</label>
<br>
<button @click="$store.commit('increment')">
++
</button>
<button @click="$store.commit('decrement')">
--
</button>
<button @click="$store.commit('incrementBy', 6)">
+6
</button>
<button @click="$store.commit('decrementBy', { amount: 2, msg: 'count-2' })">
-2
</button>
<button @click="$store.commit('changeTitle', '我是 son1 标题')">
更改 title
</button>
</div>
</template>
<style lang="css" scoped>
.box {
border: 3px solid #ccc;
width: 400px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 20px;
}
h2 {
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style><script>
import { mapMutations, mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Son2Com',
computed: {
// mapState 和 mapGetters 都是映射属性
...mapState(['count']),
},
methods: {
// mapMutations 和 mapActions 都是映射方法
...mapMutations(['increment', 'decrement', 'incrementBy', 'decrementBy', 'changeTitle']),
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div class="box">
<h2>Son2 子组件</h2>
从 vuex 中获取的值:<span>{{ count }}</span>
<br>
<button @click="increment">
++
</button>
<button @click="decrement">
--
</button>
<button @click="incrementBy(6)">
+6
</button>
<button @click="decrementBy({ amount: 2, msg: 'count-2' })">
-2
</button>
<button @click="changeTitle('我是 son2 标题')">
更改 title
</button>
</div>
</template>
<style lang="css" scoped>
.box {
border: 3px solid #ccc;
width: 400px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 20px;
}
h2 {
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>Action 异步操作
Action 类似于 mutation,不同在于:
- Action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态。
- Action 可以包含任意异步操作。
分发 Action
Action 通过 store.dispatch 方法触发:store.dispatch('increment')
乍一眼看上去感觉多此一举,我们直接分发 mutation 岂不更方便?实际上并非如此,还记得 mutation 必须同步执行这个限制么?Action 就不受约束!我们可以在 action 内部执行异步操作:
actions: {
incrementAsync ({ commit }) {
setTimeout(() => {
commit('increment')
}, 1000)
}
}Actions 支持同样的载荷方式和对象方式进行分发:
// 以载荷形式分发
store.dispatch('incrementAsync', {
amount: 10,
})
// 以对象形式分发
store.dispatch({
type: 'incrementAsync',
amount: 10,
})来看一个更加实际的购物车示例,涉及到调用异步 API 和分发多重 mutation:
actions: {
checkout ({ commit, state }, products) {
// 把当前购物车的物品备份起来
const savedCartItems = [...state.cart.added]
// 发出结账请求,然后乐观地清空购物车
commit(types.CHECKOUT_REQUEST)
// 购物 API 接受一个成功回调和一个失败回调
shop.buyProducts(
products,
// 成功操作
() => commit(types.CHECKOUT_SUCCESS),
// 失败操作
() => commit(types.CHECKOUT_FAILURE, savedCartItems)
)
}
}注意我们正在进行一系列的异步操作,并且通过提交 mutation 来记录 action 产生的副作用(即状态变更)。
mapActions 辅助函数
- 在组件中使用
this.$store.dispatch('xxx')分发 action - 使用
mapActions辅助函数将组件的 methods 映射为store.dispatch调用(需要先在根节点注入store)
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
methods: {
...mapActions([
'increment', // 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
// `mapActions` 也支持载荷:
'incrementBy', // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
...mapActions({
add: 'increment', // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
}),
},
}示例代码
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
strict: process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production',
state: {
count: 101,
title: '我是 store 中的标题',
},
mutations: {
changeTitle(state, title) {
state.title = title
},
changeCount(state, count) {
state.count = count
},
},
// actions 处理异步
// 不能直接操作 state,操作 state,还是需要 mutation commit 来操作
actions: {
changeTitleAction({ commit }, title) {
setTimeout(() => {
commit('changeTitle', title)
}, 1000)
},
changeCountAction(context, count) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('changeCount', count)
}, 2000)
},
},
})
export default store<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Son1Com',
computed: {
...mapState(['count']),
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div class="box">
<h2>Son1 子组件</h2>
从 vuex 中获取的值:<label>{{ count }}</label>
<br>
<button @click="$store.dispatch('changeTitleAction', '我是 son1 标题')">
1s 后更改 title
</button>
<button @click="$store.dispatch('changeCountAction', 99)">
2s 后更改 count 为 99
</button>
</div>
</template>
<style lang="css" scoped>
.box {
border: 3px solid #ccc;
width: 400px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 20px;
}
h2 {
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style><script>
import { mapActions, mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Son2Com',
computed: {
// mapState 和 mapGetters 都是映射属性
...mapState(['count']),
},
methods: {
// mapMutations 和 mapActions 都是映射方法
...mapActions(['changeTitleAction', 'changeCountAction']),
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div class="box">
<h2>Son2 子组件</h2>
从 vuex 中获取的值:<span>{{ count }}</span>
<br>
<button @click="changeTitleAction('我是 son2 标题')">
1s 后更改 title
</button>
<button @click="changeCountAction(88)">
2s 后更改 count 为 88
</button>
</div>
</template>
<style lang="css" scoped>
.box {
border: 3px solid #ccc;
width: 400px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 20px;
}
h2 {
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style>Module
由于使用单一状态树,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象。当应用变得非常复杂时,store 对象就有可能变得相当臃肿。
为了解决以上问题,Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块——从上至下进行同样方式的分割:
jsconst moduleA = { state: () => ({ ... }), mutations: { ... }, actions: { ... }, getters: { ... } } const moduleB = { state: () => ({ ... }), mutations: { ... }, actions: { ... } } const store = new Vuex.Store({ modules: { a: moduleA, b: moduleB } }) store.state.a // -> moduleA 的状态 store.state.b // -> moduleB 的状态
模块的局部状态
对于模块内部的 mutation 和 getter,接收的第一个参数是模块的局部状态对象。
const moduleA = {
state: () => ({
count: 0,
}),
mutations: {
increment(state) {
// 这里的 `state` 对象是模块的局部状态
state.count++
},
},
getters: {
doubleCount(state) {
return state.count * 2
},
},
}同样,对于模块内部的 action,局部状态通过 context.state 暴露出来,根节点状态则为 context.rootState:
const moduleA = {
// ...
actions: {
incrementIfOddOnRootSum({ state, commit, rootState }) {
if ((state.count + rootState.count) % 2 === 1) {
commit('increment')
}
},
},
}对于模块内部的 getter,根节点状态会作为第三个参数暴露出来:
const moduleA = {
// ...
getters: {
sumWithRootCount(state, getters, rootState) {
return state.count + rootState.count
},
},
}命名空间
默认情况下,模块内部的 action、mutation 和 getter 是注册在全局命名空间的——这样使得多个模块能够对同一 mutation 或 action 作出响应。
如果希望你的模块具有更高的封装度和复用性,你可以通过添加
namespaced: true的方式使其成为带命名空间的模块。当模块被注册后,它的所有 getter、action 及 mutation 都会自动根据模块注册的路径调整命名。例如:jsconst store = new Vuex.Store({ modules: { account: { namespaced: true, // 模块内容(module assets) state: () => ({ ... }), // 模块内的状态已经是嵌套的了,使用 `namespaced` 属性不会对其产生影响 getters: { isAdmin () { ... } // -> getters['account/isAdmin'] }, actions: { login () { ... } // -> dispatch('account/login') }, mutations: { login () { ... } // -> commit('account/login') }, // 嵌套模块 modules: { // 继承父模块的命名空间 myPage: { state: () => ({ ... }), getters: { profile () { ... } // -> getters['account/profile'] } }, // 进一步嵌套命名空间 posts: { namespaced: true, state: () => ({ ... }), getters: { popular () { ... } // -> getters['account/posts/popular'] } } } } } })启用了命名空间的 getter 和 action 会收到局部化的
getter,dispatch和commit。换言之,你在使用模块内容(module assets)时不需要在同一模块内额外添加空间名前缀。更改namespaced属性后不需要修改模块内的代码。
在带命名空间的模块注册全局 action
若需要在带命名空间的模块注册全局 action,你可添加 root: true,并将这个 action 的定义放在函数 handler 中。例如:
{
actions: {
someOtherAction ({dispatch}) {
dispatch('someAction')
}
},
modules: {
foo: {
namespaced: true,
actions: {
someAction: {
root: true,
handler (namespacedContext, payload) { ... } // -> 'someAction'
}
}
}
}
}带命名空间的绑定函数
当使用 mapState, mapGetters, mapActions 和 mapMutations 这些函数来绑定带命名空间的模块时,写起来可能比较繁琐:
computed: {
...mapState({
a: state => state.some.nested.module.a,
b: state => state.some.nested.module.b
})
},
methods: {
...mapActions([
'some/nested/module/foo', // -> this['some/nested/module/foo']()
'some/nested/module/bar' // -> this['some/nested/module/bar']()
])
}对于这种情况,你可以将模块的空间名称字符串作为第一个参数传递给上述函数,这样所有绑定都会自动将该模块作为上下文。于是上面的例子可以简化为:
computed: {
...mapState('some/nested/module', {
a: state => state.a,
b: state => state.b
})
},
methods: {
...mapActions('some/nested/module', [
'foo', // -> this.foo()
'bar' // -> this.bar()
])
}而且,你可以通过使用 createNamespacedHelpers 创建基于某个命名空间辅助函数。它返回一个对象,对象里有新的绑定在给定命名空间值上的组件绑定辅助函数:
import { createNamespacedHelpers } from 'vuex'
const { mapState, mapActions } = createNamespacedHelpers('some/nested/module')
export default {
computed: {
// 在 `some/nested/module` 中查找
...mapState({
a: (state) => state.a,
b: (state) => state.b,
}),
},
methods: {
// 在 `some/nested/module` 中查找
...mapActions(['foo', 'bar']),
},
}示例代码
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import cart from './modules/cart'
import info from './modules/info'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
strict: process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production',
modules: {
info,
cart,
},
})
export default storeconst state = {
cartList: [
{ id: 1, title: 'iPad 4 Mini', price: 500.01, inventory: 2 },
{ id: 2, title: 'H&M T-Shirt White', price: 10.99, inventory: 10 },
{ id: 3, title: 'Charlie XCX - Sucker CD', price: 19.99, inventory: 5 },
],
totalNum: 0,
totalPrice: 0,
}
const getters = {
cartProducts: (state) => {
return state.cartList.map((item) => {
return {
id: item.id,
title: item.title,
price: item.price,
inventory: item.inventory,
}
})
},
cartTotalNum: (state) => {
return state.cartList.reduce((total, item) => {
return total + item.inventory
}, 0)
},
cartTotalPrice: (state) => {
return state.cartList.reduce((total, item) => {
return total + item.price * item.inventory
}, 0)
},
}
const mutations = {
decrementProductInventory(state, id) {
const product = state.cartList.find(item => item.id === id)
if (product && product.inventory > 0)
product.inventory--
},
incrementProductInventory(state, id) {
const product = state.cartList.find(item => item.id === id)
if (product)
product.inventory++
},
editProductInventory(state, { id, inventory }) {
const product = state.cartList.find(item => item.id === id)
if (product && inventory >= 1)
product.inventory = inventory
},
}
const actions = {
editProductInventoryAction({ commit }, { id, inventory }) {
setTimeout(() => {
commit('editProductInventory', { id, inventory })
}, 1000)
},
}
export default {
namespaced: true,
state,
getters,
mutations,
actions,
}const state = {
vueInfo: {
name: 'Vue2',
version: '2.7.0',
},
title: '我是 info module 中的标题',
}
const getters = {
UpperCaseTitle(state) {
return state.title.toUpperCase()
},
RemoveVersionDot: (state) => {
return state.vueInfo.version.replace(/\./g, '')
},
}
const mutations = {
changeTitle(state, title) {
state.title = title
},
changeVueInfo(state, vueInfo) {
state.vueInfo = vueInfo
},
}
const actions = {
changeTitleAction({ commit }, title) {
setTimeout(() => {
commit('changeTitle', title)
}, 1000)
},
changeVueInfoAction({ commit }, vueInfo) {
setTimeout(() => {
commit('changeVueInfo', vueInfo)
}, 1000)
},
}
export default {
// namespaced 命名空间, 使得模块中的 action 和 mutation 都具有模块名前缀
namespaced: true,
state,
getters,
mutations,
actions,
}<script>
import { mapActions, mapGetters, mapMutations, mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Son1Com',
computed: {
...mapState('info', ['vueInfo', 'title']),
...mapGetters('info', ['UpperCaseTitle', 'RemoveVersionDot']),
},
methods: {
...mapMutations('info', ['changeTitle', 'changeVueInfo']),
...mapActions('info', ['changeTitleAction', 'changeVueInfoAction']),
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div class="box">
<h3>Son1 子组件 {{ title }}</h3>
从 vuex 中获取的值:
<p>
属性<br>
vueInfo: <span>{{ vueInfo }}</span> <br>
vueInfo.name: <span>{{ vueInfo.name }}</span> <br>
vueInfo.version: <span>{{ vueInfo.version }}</span> <br>
title: <span>{{ title }}</span> <br>
UpperCaseTitle: <span>{{ UpperCaseTitle }}</span> <br>
RemoveVersionDot: <span>{{ RemoveVersionDot }}</span> <br>
</p>
<p>
方法<br>
Mutations:
<button @click="changeTitle('vue3')">
修改 title
</button>
<button @click="changeVueInfo({ name: 'vue3', version: '3.4.15' })">
修改 vueInfo
</button>
<br><br>
Action:
<button @click="changeTitleAction('我是 info module 中的标题')">
1s后恢复 title
</button>
<button @click="changeVueInfoAction({ name: 'vue2', version: '2.6.14' })">
1s后恢复 vueInfo
</button>
<br>
</p>
</div>
</template>
<style lang="css" scoped>
.box {
border: 3px solid #ccc;
width: 400px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 20px;
}
h2 {
margin-top: 10px;
}
</style><script>
import { mapActions, mapGetters, mapMutations, mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Son2Com',
computed: {
...mapState('cart', ['cartList']),
...mapGetters('cart', ['cartProducts', 'cartTotalNum', 'cartTotalPrice']),
},
methods: {
...mapMutations('cart', [
'decrementProductInventory',
'incrementProductInventory',
'editProductInventory',
]),
...mapActions('cart', ['editProductInventoryAction']),
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div class="box">
<h2>Son2 子组件</h2>
从 vuex 中获取的值:
<br>
<table>
<tr>
<th>id</th>
<th>名称</th>
<th>价格</th>
<th>存量</th>
<th>总额</th>
</tr>
<tr v-for="product in cartProducts" :key="product.id">
<td>{{ product.id }}</td>
<td>{{ product.title }}</td>
<td>{{ product.price }}</td>
<td>
<button @click="decrementProductInventory(product.id)">
-
</button>
{{ product.inventory }}
<button @click="incrementProductInventory(product.id)">
+
</button>
</td>
<td>{{ (product.price * product.inventory).toFixed(2) }}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="3">
总计
</td>
<td>{{ cartTotalNum }}</td>
<td>{{ cartTotalPrice.toFixed(2) }}</td>
</tr>
</table>
<br>
<p>
方法<br>
Mutations:
<button
@click="
editProductInventory({
id: 1,
inventory: 10,
})
"
>
修改 id 为 1 的商品库存为 10
</button>
<br><br>
Action:
<button
@click="
editProductInventoryAction({
id: 2,
inventory: 20,
})
"
>
1s后修改 id 为 2 的商品库存为 20
</button>
<br>
</p>
</div>
</template>
<style lang="css" scoped>
.box {
border: 3px solid #ccc;
width: 500px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 20px;
}
h2 {
margin-top: 10px;
}
table {
width: 100%;
border-collapse: collapse;
}
th,
td {
border: 1px solid #ccc;
padding: 5px;
}
</style><script>
import Son1 from './components/Son1.vue'
import Son2 from './components/Son2.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
Son1,
Son2,
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>根组件</h1>
<Son1 />
<hr>
<Son2 />
<hr>
</div>
</template>
<style>
#app {
width: 600px;
margin: 20px auto;
border: 3px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 3px;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>表单处理
// store/index.js
mutations: {
updateMessage (state, message) {
state.obj.message = message
}
}使用 :value + @input
给 <input> 中绑定 value,然后侦听 input 或者 change 事件,在事件回调中调用一个方法 updateMessage
// 组件中
<input :value="message" @input="updateMessage">
// ...
computed: {
...mapState({
message: state => state.obj.message
})
},
methods: {
updateMessage (e) {
this.$store.commit('updateMessage', e.target.value)
}
}示例代码
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
strict: process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production',
state: {
count: 101,
title: '我是 store 中的标题',
},
mutations: {
changeTitle(state, title) {
state.title = title
},
changeCount(state, count) {
state.count = count
},
},
})
<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
import Son1 from './components/Son1.vue'
import Son2 from './components/Son2.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
Son1,
Son2,
},
computed: {
...mapState(['title', 'count']),
...mapState({
title: state => state.title,
}),
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>根组件 - {{ title }} - {{ count }}</h1>
<input
type="text"
:value="title"
@input="$store.commit('changeTitle', $event.target.value)"
>
<Son1 />
<hr>
<Son2 />
<hr>
</div>
</template>
<style>
#app {
width: 600px;
margin: 20px auto;
border: 3px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 3px;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>使用双向绑定计算属性
使用带有 setter 的双向绑定计算属性
// 组件中
<input v-model="message">
// ...
computed: {
message: {
get () {
return this.$store.state.obj.message
},
set (value) {
this.$store.commit('updateMessage', value)
}
}
}示例代码
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
strict: process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production',
state: {
count: 101,
title: '我是 store 中的标题',
},
mutations: {
changeTitle(state, title) {
state.title = title
},
changeCount(state, count) {
state.count = count
},
},
})
<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
import Son1 from './components/Son1.vue'
import Son2 from './components/Son2.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
Son1,
Son2,
},
computed: {
...mapState(['title', 'count']),
title: {
get() {
return this.$store.state.title
},
set(value) {
this.$store.commit('changeTitle', value)
},
},
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>根组件 - {{ title }} - {{ count }}</h1>
<input
v-model="title"
type="text"
>
<Son1 />
<hr>
<Son2 />
<hr>
</div>
</template>
<style>
#app {
width: 600px;
margin: 20px auto;
border: 3px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 3px;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>Vuex 模块化 使用小结
项目结构
Vuex 并不限制你的代码结构。但是,它规定了一些需要遵守的规则:
- 应用层级的状态应该集中到单个 store 对象中。
- 提交 mutation 是更改状态的唯一方法,并且这个过程是同步的。
- 异步逻辑都应该封装到 action 里面。
只要你遵守以上规则,如何组织代码随你便。如果你的 store 文件太大,只需将 action、mutation 和 getter 分割到单独的文件。
├── index.html
├── main.js
├── api
│ └── ... # 抽取出API请求
├── components
│ ├── App.vue
│ └── ...
└── store
├── index.js # 我们组装模块并导出 store 的地方
├── actions.js # 根级别的 action
├── mutations.js # 根级别的 mutation
└── modules
├── cart.js # 购物车模块
└── products.js # 产品模块请参考 购物车示例
直接使用
state-->$store.state.模块名.数据项名getters-->$store.getters['模块名/属性名']mutations-->$store.commit('模块名/方法名', 其他参数)actions-->$store.dispatch('模块名/方法名', 其他参数)
借助辅助方法使用
// store/index.js
// mapState 和 mapGetters 都是映射属性
// mapMutations 和 mapActions 都是映射方法
computed、methods: {
...mapXxxx('模块名', ['数据项 | 方法']),
...mapXxxx('模块名', { 新的名字: 原来的名字 }),
}
// 组件中导入
import { mapState, mapMutations, mapActions, mapGetters } from 'vuex'组件中直接使用 属性 {{ age }} 或 方法 @click="updateAge(2)"
综合案例 购物车
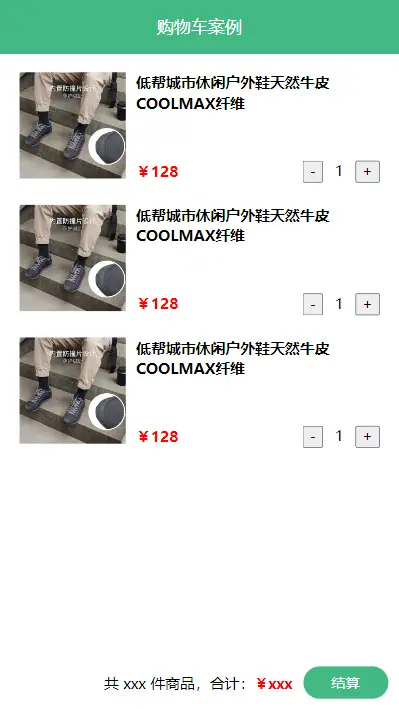
需求:
- 发请求动态渲染购物车,数据存 vuex(存 cart 模块,将来还会有 user 模块,article 模块...)
- 数字框可以修改数据
- 动态计算总价和总数量
创建项目
使用
create-vue创建项目bashpnpm create vue@legacy删除
src目录下所有文件,替换成教学资料的《vuex-cart-准备代码》手动安装 vuex3
bashpnpm add vuex@3安装 less 预处理器
bashpnpm add less less-loader -D此时项目目录
bash❯ tre -E node_modules . ├── public │ └── favicon.ico ├── src │ ├── App.vue │ ├── components │ │ ├── cart-footer.vue │ │ ├── cart-header.vue │ │ └── cart-item.vue │ ├── main.js │ └── store │ └── index.js ├── eslint.config.js ├── index.html ├── package.json ├── pnpm-lock.yaml └── vite.config.js
示例代码
<script>
export default {
name: 'CartFooter',
}
</script>
<template>
<div class="footer-container">
<!-- 中间的合计 -->
<div>
<span>共 xxx 件商品,合计:</span>
<span class="price">¥xxx</span>
</div>
<!-- 右侧结算按钮 -->
<button class="btn btn-success btn-settle">
结算
</button>
</div>
</template>
<style lang="less" scoped>
.footer-container {
background-color: white;
height: 50px;
border-top: 1px solid #f8f8f8;
display: flex;
justify-content: flex-end;
align-items: center;
padding: 0 10px;
position: fixed;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
width: 100%;
z-index: 999;
}
.price {
color: red;
font-size: 13px;
font-weight: bold;
margin-right: 10px;
}
.btn-settle {
height: 30px;
min-width: 80px;
margin-right: 20px;
border-radius: 20px;
background: #42b983;
border: none;
color: white;
}
</style><script>
export default {
name: 'CartHeader',
}
</script>
<template>
<div class="header-container">
购物车案例
</div>
</template>
<style lang="less" scoped>
.header-container {
height: 50px;
line-height: 50px;
font-size: 16px;
background-color: #42b983;
text-align: center;
color: white;
position: fixed;
top: 0;
left: 0;
width: 100%;
z-index: 999;
}
</style><script>
export default {
name: 'CartItem',
methods: {
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div class="goods-container">
<!-- 左侧图片区域 -->
<div class="left">
<img src="https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/3a56a913e687dc2279473e325ea770a9.jpg" class="avatar" alt="">
</div>
<!-- 右侧商品区域 -->
<div class="right">
<!-- 标题 -->
<div class="title">
低帮城市休闲户外鞋天然牛皮 COOLMAX 纤维
</div>
<div class="info">
<!-- 单价 -->
<span class="price">¥128</span>
<div class="btns">
<!-- 按钮区域 -->
<button class="btn btn-light">
-
</button>
<span class="count">1</span>
<button class="btn btn-light">
+
</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<style lang="less" scoped>
.goods-container {
display: flex;
padding: 10px;
+ .goods-container {
border-top: 1px solid #f8f8f8;
}
.left {
.avatar {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
margin-right: 10px;
}
.right {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: space-between;
flex: 1;
.title {
font-weight: bold;
}
.info {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
.price {
color: red;
font-weight: bold;
}
.btns {
.count {
display: inline-block;
width: 30px;
text-align: center;
}
}
}
}
}
.custom-control-label::before,
.custom-control-label::after {
top: 3.6rem;
}
</style><script>
import CartHeader from '@/components/cart-header.vue'
import CartFooter from '@/components/cart-footer.vue'
import CartItem from '@/components/cart-item.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
CartHeader,
CartFooter,
CartItem,
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div class="app-container">
<!-- Header 区域 -->
<CartHeader />
<!-- 商品 Item 项组件 -->
<CartItem />
<CartItem />
<CartItem />
<!-- Footer 区域 -->
<CartFooter />
</div>
</template>
<style lang="less" scoped>
.app-container {
padding: 50px 0;
font-size: 14px;
}
</style>import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import store from './store'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
store,
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
},
getters: {
},
mutations: {
},
actions: {
},
modules: {
},
})构建 vuex-cart 模块
- store 下创建 cart 模块。
- 挂载到 vuex store 中。
示例代码
const state = {
cartList: [],
}
const mutations = {
}
const actions = {
}
const getters = {
}
export default {
namespaced: true,
state,
mutations,
actions,
getters,
}import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import cart from './modules/cart'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
cart,
},
})准备后端接口服务环境
json-server是一款小巧的接口模拟工具,一分钟内就能搭建一套 Restful 风格的 API,尤其适合前端接口测试使用。- 只需指定一个
json文件作为api的数据源即可,使用起来非常方便,30 秒入门。 - 进阶操作还支持分页,排序等操作,简直强大。
安装
json-serverbashpnpm add json-server -D准备数据。创建
db目录,将资料db.json移入db目录。启动
json-server接口服务器bash❯ pnpm dlx json-server db/db.json --watch --port 5678 Packages: +54 ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ Progress: resolved 55, reused 54, downloaded 0, added 54, done --watch/-w can be omitted, JSON Server 1+ watches for file changes by default JSON Server started on PORT :5678 Press CTRL-C to stop Watching db.json... (˶ᵔ ᵕ ᵔ˶) Index: http://localhost:5678/ Static files: Serving ./public directory if it exists Endpoints: http://localhost:5678/cart浏览器访问
http://localhost:5678/cart可以查看db.json内容。如果您发出 POST、PUT、PATCH 或 DELETE 请求,更改将自动安全地保存到
db.json文件中。
示例代码
db.json
{
"cart": [
{
"id": "100001",
"name": "低帮城市休闲户外鞋天然牛皮 COOLMAX 纤维",
"price": 128,
"count": 1,
"thumb": "https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/3a56a913e687dc2279473e325ea770a9.jpg"
},
{
"id": "100002",
"name": "网易味央黑猪猪肘 330g*1 袋",
"price": 39,
"count": 10,
"thumb": "https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/d0a56474a8443cf6abd5afc539aa2476.jpg"
},
{
"id": "100003",
"name": "KENROLL 男女简洁多彩一片式室外拖",
"price": 128,
"count": 10,
"thumb": "https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/eb1556fcc59e2fd98d9b0bc201dd4409.jpg"
},
{
"id": "100004",
"name": "云音乐定制 IN 系列 intar 民谣木吉他",
"price": 589,
"count": 1,
"thumb": "https://yanxuan-item.nosdn.127.net/4d825431a3587edb63cb165166f8fc76.jpg"
}
]
}请求动态渲染数据
请求获取数据存入 vuex, 映射渲染

- 安装 axios。
pnpm add axios - cart 模块中准备 actions 和 mutations。
- actions 中使用 axios 向接口
json-server请求数据 - mutations 中更新购物车列表
- actions 中使用 axios 向接口
App.vue页面中使用 action, 从而实现将数据存入 vuex 中。- 使用
mapActions辅助函数将组件的 methods 映射为store.dispatch调用(需要先在根节点注入store) - 在组件中使用
this.$store.dispatch('xxx')分发 action
- 使用
- 使用 v-for 遍历数据进行动态渲染。
App.vue中<cart-item v-for="item in list" :key="item.id" :item="item"></cart-item>向子组件传递item数据cart-item.vue中使用props接受数据。
示例代码
import axios from 'axios'
const state = {
cartList: [],
}
const mutations = {
updateCartList(state, payload) {
state.cartList = payload
},
}
<script>
import { mapActions, mapState } from 'vuex'
import CartHeader from '@/components/cart-header.vue'
import CartFooter from '@/components/cart-footer.vue'
import CartItem from '@/components/cart-item.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
CartHeader,
CartFooter,
CartItem,
},
computed: {
...mapState('cart', ['cartList']),
},
created() {
// 从服务器获取购物车列表数据,并将数据保存到 Vuex store 的状态中
this.$store.dispatch('cart/getCartList')
},
methods: {
...mapActions('cart', ['getCartList']),
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div class="app-container">
<!-- Header 区域 -->
<CartHeader />
<!-- 商品 Item 项组件 -->
<CartItem v-for="item in cartList" :key="item.id" :item="item" />
<!-- Footer 区域 -->
<CartFooter />
</div>
</template>
<style lang="less" scoped>
.app-container {
padding: 50px 0;
font-size: 14px;
}
</style><script>
export default {
name: 'CartItem',
props: {
item: {
type: Object,
required: true,
},
},
methods: {},
}
</script>
<template>
<div class="goods-container">
<!-- 左侧图片区域 -->
<div class="left">
<img :src="item.thumb" alt="" class="avatar" referrerpolicy="no-referrer">
</div>
<!-- 右侧商品区域 -->
<div class="right">
<!-- 标题 -->
<div class="title">
{{ item.name }}
</div>
<div class="info">
<!-- 单价 -->
<span class="price">¥{{ item.price }}</span>
<div class="btns">
<!-- 按钮区域 -->
<button class="btn btn-light">
-
</button>
<span class="count">{{ item.count }}</span>
<button class="btn btn-light">
+
</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<style lang="less" scoped>
.goods-container {
display: flex;
padding: 10px;
+ .goods-container {
border-top: 1px solid #f8f8f8;
}
.left {
.avatar {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
margin-right: 10px;
}
.right {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: space-between;
flex: 1;
.title {
font-weight: bold;
}
.info {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
.price {
color: red;
font-weight: bold;
}
.btns {
.count {
display: inline-block;
width: 30px;
text-align: center;
}
}
}
}
}
.custom-control-label::before,
.custom-control-label::after {
top: 3.6rem;
}
</style>修改数量

- cart 模块中准备 actions 和 mutations。
cart-item.vue页面中使用 action, 从而实现将数据存入 vuex 中。- 使用
mapActions辅助函数将组件的 methods 映射为store.dispatch调用
- 使用
cart-item.vue页面中 button 注册点击事件。- 当
item.count === 1时禁用减少数量按钮
- 当
示例代码
import axios from 'axios'
const state = {
cartList: [],
}
const mutations = {
updateCartList(state, payload) {
state.cartList = payload
},
updateCartItem(state, { id, count }) {
const item = state.cartList.find(item => item.id === id)
item.count = count
},
}
const actions = {
async getCartList({ commit }) {
const { data } = await axios.get('http://localhost:5678/cart')
commit('updateCartList', data)
},
async updateCartItem({ commit }, { id, count }) {
await axios.patch(`http://localhost:5678/cart/${id}`, {
count,
})
commit('updateCartItem', { id, count })
},
}
const getters = {}
export default {
namespaced: true,
state,
mutations,
actions,
getters,
}<script>
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
商品总数和总价
- cart 模块中准备 getters
- 使用
mapGetters辅助函数将 store 中的 getter 映射到局部计算属性 cart-footer.vue页面中渲染
示例代码
import axios from 'axios'
const state = {
cartList: [],
}
const mutations = {
updateCartList(state, payload) {
state.cartList = payload
},
updateCartItem(state, { id, count }) {
const item = state.cartList.find(item => item.id === id)
item.count = count
},
}
const actions = {
async getCartList({ commit }) {
const { data } = await axios.get('http://localhost:5678/cart')
commit('updateCartList', data)
},
async updateCartItem({ commit }, { id, count }) {
await axios.patch(`http://localhost:5678/cart/${id}`, {
count,
})
commit('updateCartItem', { id, count })
},
}
const getters = {
cartTotal(state) {
return state.cartList.reduce((total, item) => total + item.price * item.count, 0)
},
cartCount(state) {
return state.cartList.reduce((total, item) => total + item.count, 0)
},
}
<script>
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'